INFORMATIVE
INFORMATIVE
INFORMATIVE

INFORMATIVE
INFORMATIVE
Lamination
Lamination
We carry out the entire production cycle: starting from the lamination of carbon fiber, Kevlar, and glass fabrics, up to the subsequent processes of cutting, shaping, and composition into sandwich panels.
Our production process

Fabric cutting
The pre-preg fabrics in rolls are laid out and cut with an automated system to the sizes required for lamination.
Milling
The pieces are cut, drilled and milled using a CNC machining center.
Molding cycle
Lamination takes place with a double press system:
First hot press that allows control of temperature, pressure, and the necessary degassing cycles. The maximum operating temperature can reach up to 180° degrees; the maximum operating pressure is between 9 and 13 Kg/cm;
Second cold press with cryogenic system stabilizes and completes the polymerization cycle of the fabric matrices.


SPECIAL APPLICATIONS
Thermoforming
Hot molding of materials, starting from sheets or film, under pressure or vacuum.
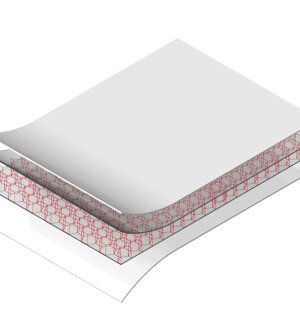
Panel creation
Production of a panel with a support in aluminum or Nomex® honeycomb and one or both skins coated in FIBER-SKIN
Products


FIBER-SKIN
Lamination of multiple layers of composite fabrics
Creation of a composite skin.
Choice of the type of fabrics, even different from each other, and their number, to be defined based on the desired result.
FIBER-APP
Creation of panel with FIBER-SKIN covering
Production of a panel with a core made of aluminum or Nomex® honeycomb and one or both faces covered with FIBER-SKIN.
Materials
Fabrics
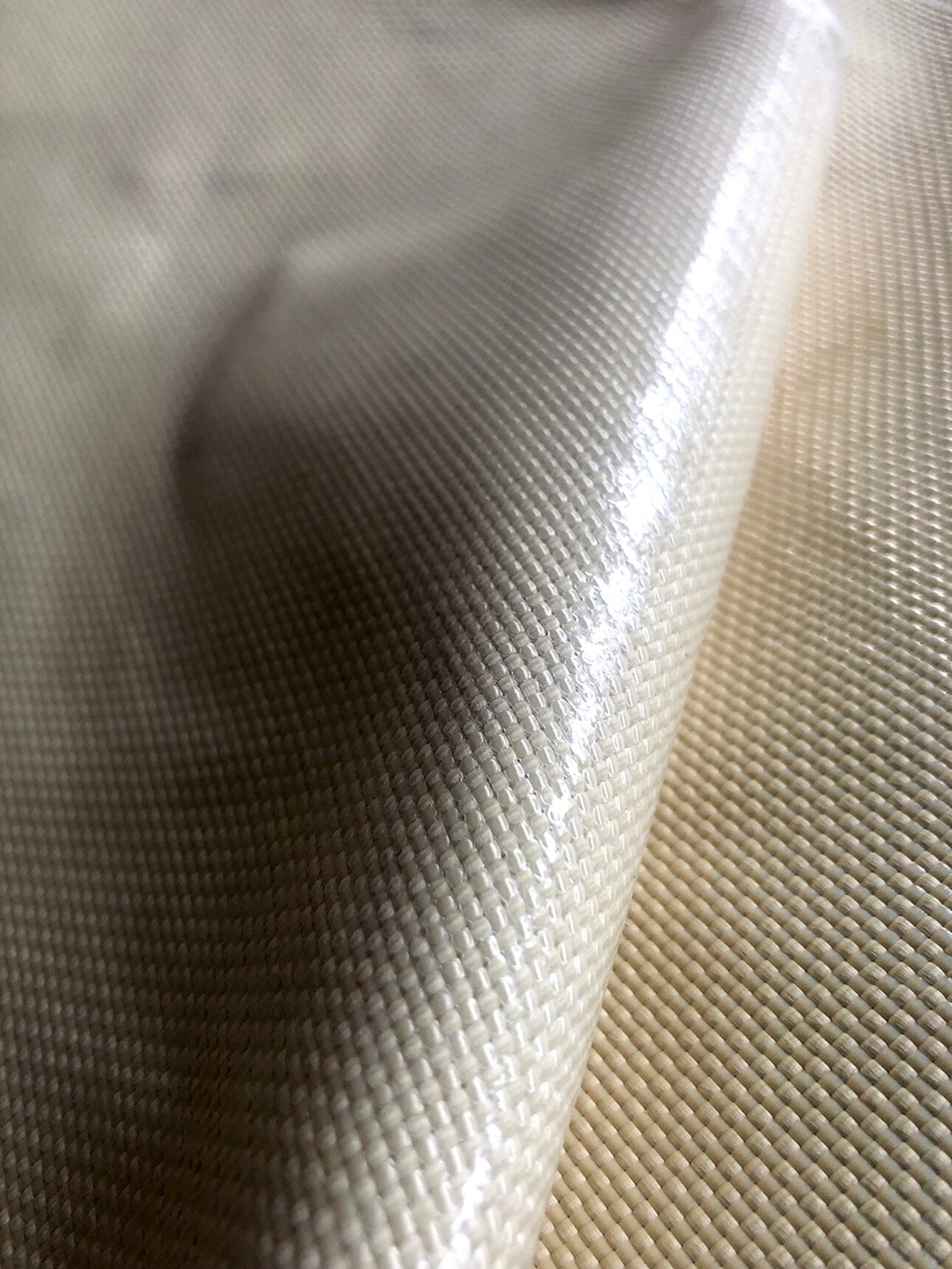

Pre-impregnated fabrics
Pre-impregnated fabrics are made with all compatible types of fabric, from polyester to carbon fiber, through the application of resins, generally epoxy.
Shielding pre-impregnated fabrics
Compared to other pre-impregnated fabrics, shielding pre-impregnated fabrics have an additional “nickel plating bath” that gives the pre-impregnated fabric high shielding properties. These properties provide protection from electromagnetic waves.
Fabrics coupled with polyethylene.
These are dry fabrics coupled with a thermoplastic polyethylene film

Fibre composite
Glass fibers. In structural fabrics, glass fibers are characterized by excellent elasticity, high mechanical strength, and low density.
Kevlar fibers. Kevlar fibers are characterized by remarkable resistance to traction, impacts, and corrosion. In addition, Kevlar laminates are not electrically conductive and are heat resistant.
Carbon fibers. Carbon fibers are characterized by high mechanical strength for the same weight, resistance to chemical agents, and excellent fire-retardant properties.
Polyethylene bonded fabrics. These are dry fabrics bonded with a thermoplastic polyethylene film.


Resins
Thermosetting resins have a non-reversible heat-activated polymerization process. In general, thermosetting resins provide mechanical properties such as low shrinkage during molding, resistance to chemical agents (acids, bases, solvents), temperature resistance, low dielectric constant, and excellent adhesion to metals and fibers.
Thermoplastic resins are characterized by a change of state, from plastic to rigid and vice versa, which can be reactivated by heat. This allows fabrics coupled with these resins to be thermoformed.
